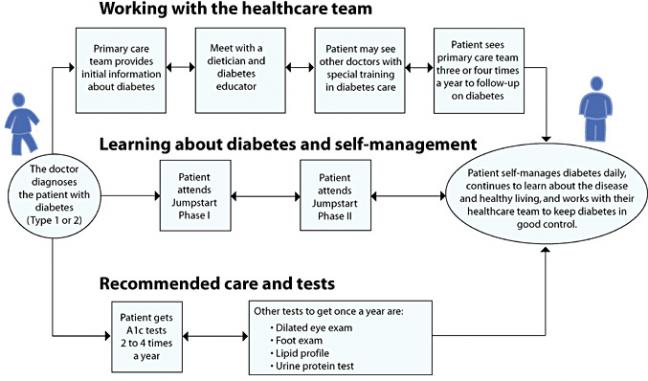
Ideally, patients with diabetes travel along several paths at the same time while taking care of their disease. These paths include:
- Working with the health care team
- Learning about diabetes and self-management
- Getting recommended care and tests
- Keeping diabetes under control
Working with the health care team
Your health care team is here to help you learn how to manage your diabetes. Your health care team includes:
- Primary care team: The health care team will talk with you about the basics of diabetes and give you information about the disease. Some of our patients have recommended websites that may be useful.
- Dietitian and diabetes educator: Your primary care provider will refer you to meet with a dietician to learn about what you can eat. The physician will also refer you to see a diabetes educator to learn about managing diabetes.
- Other doctors with special training in diabetes care: Patients with diabetes sometimes have more specialized care to manage their disease. Some of the specialists you might see are:
- Cardiologist
- Endocrinologist
- Ophthalmologist
- Podiatrist
- Psychologist
- Vascular surgeon
- Follow-ups with primary care team: Patients with diabetes should see their primary care team three to four times each year. At each visit you will have your weight and blood pressure measured.
Recommended care and tests
Uncontrolled diabetes can damage the small blood vessels and nerves of the body, including those in the brain, eyes, heart, kidneys, and feet. This is why routine tests and checkups are especially important.
- A1c (glycohemoglobin, or blood sugar) test: The A1c test measures a person's average blood sugar level over the last three months. The goal of diabetes care is to maintain the A1c below 7.0. Patients with diabetes should have their A1c tested four times each year. Once the A1c levels are stable, your physician may only order the test twice a year.
- Dilated eye exam: Diabetes is the leading cause of adult blindness in the United States. People with diabetes should see their eye doctor every year to check for any signs of retinopathy, or injury to the retina (the back of the eye).
- Foot exam: Many people with diabetes suffer from neuropathy (injury to the nerves), which typically begins with slight numbness in the feet. This loss of sensation means that many people with diabetes do not feel small foot injuries, and risk frequent infections. Because diabetes is the leading cause of non-traumatic foot amputations in the United States, people with diabetes should have their feet examined by their family doctor at each visit.
- Lipid profile (cholesterol test): Controlling your cholesterol levels can help reduce your risk for heart disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease. All people with diabetes should have a cholesterol test at least once a year. The LDL (low-density lipoprotein, or "bad" cholesterol) reading should be less than 100 for an average diabetic, but it may need to be even less if you have a history of heart disease.
- Urine protein test: Diabetes is the leading cause of permanent kidney failure in the United States. This leads to dialysis, a process in which a person requires a machine to filter their blood several times per week. To prevent kidney damage (nephropathy), all people with diabetes should have a yearly microalbumin urine test to check for early signs of diabetic injury to the kidneys.
Keeping diabetes under control
Controlling diabetes means continuing to learn about the disease and healthy living, and continuing to work with your health care team to keep diabetes in godo control.
Diabetes is a disease that needs to be managed by patients each day. They manage their diet and exercise. They can go back to the Jump Start program to learn more and refresh their knowledge and skills. Support groups are available, if patients with diabetes are interested in connecting with others who share the disease. Patients can also work with their doctor and healthcare team to learn about and take care of their diabetes.